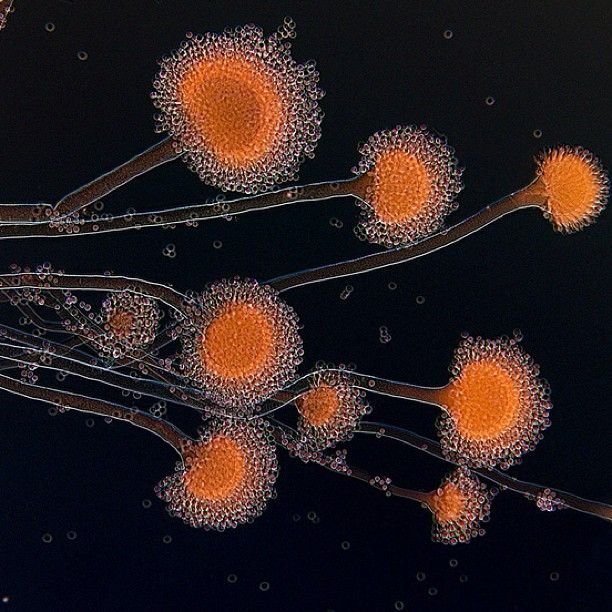
Peñiculs, though often overlooked, play a crucial role in various ecosystems and industries. Understanding these tiny organisms can provide valuable insights into soil health, agriculture, medicine, and more.
Peñiculs are microscopic fungi, bacteria, and algae that inhabit virtually every environment on Earth. Their intricate structures and diverse functions contribute to the overall balance and sustainability of ecosystems.
In soil, peñiculs aid in nutrient cycling, breaking down organic matter, and enhancing soil structure. This, in turn, promotes plant growth and improves agricultural productivity.
Peñiculs: Anatomy and Physiology
Peñi culs are microscopic fungi, bacteria, and algae that inhabit virtually every environment on Earth. Their intricate structures and diverse functions contribute to the overall balance and sustainability of ecosystems.
The Structure of Peñiculs
Peñiculs come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from single-celled organisms to complex multicellular structures. Fungal peñi culs, for example, consist of thread-like hyphae that form intricate networks known as mycelium. Bacterial peñiculs, on the other hand, are typically unicellular and vary in shape and size. Algal peñi culs can be found in both unicellular and multicellular forms, often forming colonies or filaments.
The Role of Peñiculs in Ecosystems
Peñi culs play a vital role in ecosystem dynamics, contributing to processes such as nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships.
Peñiculs in Soil Health
In soil ecosystems, peñi culs play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. Fungal peñi culs, such as mycorrhizae, form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, facilitating nutrient uptake and enhancing plant growth. Bacterial peñi culs, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can utilize, thus improving soil fertility. Algal peñi culs, through photosynthesis, contribute organic matter to the soil and help stabilize soil structure.
Peñiculs in Plant Growth
Peñi culs are essential for the health and growth of plants. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, form mutualistic relationships with plant roots, providing nutrients such as phosphorus and improving water uptake. Additionally, certain bacterial peñi culs produce plant growth-promoting substances, enhancing plant vigor and resistance to stressors such as drought and disease.
Peñiculs and Nutrient Cycling
Peñic uls play a crucial role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems. By decomposing organic matter, peñi culs release essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium back into the soil, making them available for plant uptake. This nutrient recycling process is vital for maintaining soil fertility and supporting plant growth.
Types of Peñiculs
Peñiculs encompass a diverse array of organisms, including fungi, bacteria, and algae, each with its unique characteristics and ecological roles.
Fungal Peñiculs
Fungal peñi culs, or fungi, are a diverse group of organisms that play various roles in ecosystems. From decomposing organic matter to forming symbiotic relationships with plants, fungi are essential for nutrient cycling and ecosystem functioning. Examples of fungal peñi culs include mycorrhizae, which form mutualistic associations with plant roots, and saprophytic fungi, which decompose dead organic material.
Bacterial Peñiculs
Bacterial peñiculs, or bacteria, are ubiquitous microorganisms found in virtually every environment on Earth. They play essential roles in nutrient cycling, nitrogen fixation, and decomposition. Examples of bacterial peñi culs include nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can use, and nitrifying bacteria, which convert ammonium into nitrate, an essential nutrient for plants.
Algal Peñi culs
Algal peñi culs, or algae, are photosynthetic organisms found in a wide range of aquatic and terrestrial habitats. They play crucial roles in oxygen production, nutrient cycling, and food webs. Examples of algal peñi culs include diatoms, which are important primary producers in aquatic ecosystems, and green algae, which are common in freshwater habitats.
The Impact of Peñiculs on Human Life
Peñiculs have significant implications for human health, agriculture, and industry. While some peñi culs are beneficial and essential for various processes, others can have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
Peñiculs in Agriculture
In agriculture, peñi culs play essential roles in soil fertility, plant growth, and disease suppression. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, enhance nutrient uptake and improve plant health, leading to increased crop yields. Additionally, certain bacterial peñi culs can fix atmospheric nitrogen, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Peñiculs in Medicine
Peñi culs have long been used in traditional medicine and are increasingly being explored for their potential therapeutic applications. From antibiotics to anticancer drugs, peñi culs produce a wide range of bioactive compounds with medicinal properties. However, some peñi culs can also cause human diseases and infections, highlighting the importance of understanding their biology and ecology.
Beneficial Peñiculs
Several peñi culs have proven to be valuable sources of pharmaceutical compounds and biotechnological products. For example, the fungus Penicillium produces penicillin, the first antibiotic discovered, which revolutionized modern medicine. Other examples include Streptomyces bacteria, which produce a vast array of antibiotics, and Cyanobacteria, which produce toxins with anticancer properties.
Harmful Peñiculs
Despite their many benefits, some peñi culs can pose risks to human health and the environment. Pathogenic fungi, such as Aspergillus and Candida species, can cause infections in humans and animals, leading to diseases such as aspergillosis and candidiasis. Additionally, certain cyanobacteria produce toxins known as cyanotoxins, which can contaminate water sources and pose risks to human and animal health.
The Future of Peñi culs Research
As our understanding of peñi culs continues to evolve, so too do the opportunities for research and innovation. Emerging trends in peñi culs studies hold promise for addressing pressing environmental challenges, advancing biotechnological applications, and improving human health and well-being.
Emerging Trends in Peñiculs Studies
Recent advancements in molecular biology, genomics, and bioinformatics have revolutionized our ability to study peñi culs at the molecular level. These technologies enable researchers to unravel the genetic basis of peñicul biology, identify novel bioactive compounds, and engineer peñi culs for specific applications. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches that combine ecology, microbiology, and biotechnology are providing new insights into the ecological roles and biotechnological potential of peñi culs.
Potential Applications of Peñi culs Research
The diverse biological and biochemical properties of peñi culs make them valuable resources for various applications, ranging from agriculture and bioremediation to medicine and biotechnology. By harnessing the unique capabilities of peñi culs, researchers are developing innovative solutions to global challenges, such as food security, environmental pollution, and infectious diseases. Examples of potential applications include the use of fungal peñi culs for bioremediation of contaminated environments, the exploitation of bacterial peñi culs for sustainable agriculture, and the development of novel drugs and therapies derived from peñicul metabolites.
Conclusion
In conclusion, peñi culs may be small, but their impact is profound. By studying and harnessing the power of these microorganisms, we can address environmental challenges, improve agricultural practices, and advance human health.
Also Read: Kääbntäjä
FAQs
What are peñiculs?
Peñi culs are microscopic organisms that include fungi, bacteria, and algae. They play essential roles in various ecosystems, contributing to processes such as nutrient cycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships.
How do peñi culs contribute to soil health?
Peñi culs play a crucial role in soil health by decomposing organic matter, releasing essential nutrients, and improving soil structure. Fungal peñi culs form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake, while bacterial peñiculs fix atmospheric nitrogen, promoting soil fertility.
Are there any harmful effects of peñi culs on humans?
While many peñi culs are beneficial, some can pose risks to human health. Pathogenic fungi and bacteria can cause infections in humans and animals, while certain cyanobacteria produce toxins that can contaminate water sources and pose health risks.
Can peñi culs be cultured in a laboratory setting?
Yes, peñi culs can be cultured in laboratory settings for research purposes and industrial applications. Culturing peñi culs allows scientists to study their biology, ecology, and potential biotechnological applications.
What are some practical ways to promote peñi cul growth in agriculture?
Promoting peñicul growth in agriculture can be achieved through practices such as adding organic matter to the soil, minimizing tillage, and using cover crops. Additionally, inoculating soil with beneficial peñi culs, such as mycorrhizal fungi, can enhance nutrient uptake and improve crop yields.